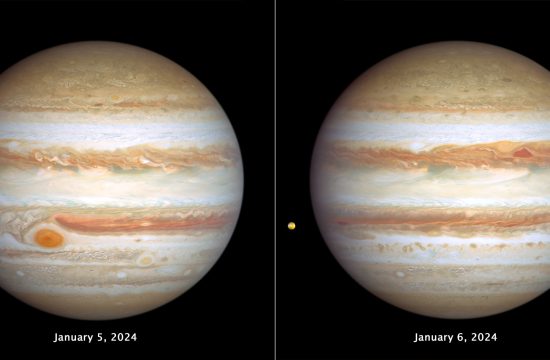
Hubble Tracks Jupiter’s Stormy Weather
The giant planet Jupiter, in all its banded glory, is revisited by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope in these latest images, taken on January 5-6, 2024, capturing both sides of the planet. Hubble monitors Jupiter and ...

Ghostly Stellar Tendrils Captured in Largest DECam Image Ever Released
With the powerful, 570-megapixel Department of Energy-fabricated Dark Energy Camera (DECam), astronomers have constructed a massive 1.3-gigapixel image showcasing the central part of the Vela Supernova Remnant, the cosmic corpse of a gigantic star that ...

NASA’s Webb, Hubble Telescopes Affirm Universe’s Expansion Rate, Puzzle Persists
When you are trying to solve one of the biggest conundrums in cosmology, you should triple check your homework. The puzzle, called the "Hubble Tension," is that the current rate of the expansion of the ...

Astronomers Measure Heaviest Black Hole Pair Ever Found
Using archival data from the Gemini North telescope, a team of astronomers have measured the heaviest pair of supermassive black holes ever found. The merging of two supermassive black holes is a phenomenon that has ...

Unveiling the Mysteries of the Solar Chromosphere with the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope
The second layer of our Sun’s atmosphere, the chromosphere, is sandwiched between the Sun’s visible surface (or photosphere) below, and its outer atmosphere (or corona) above. In this layer, plasma properties such as temperature, pressure, ...
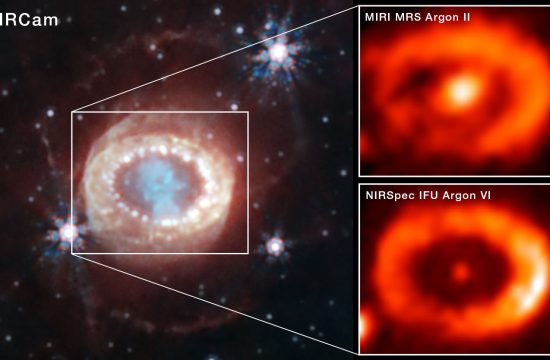
Webb Finds Evidence for Neutron Star at Heart of Young Supernova Remnant
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has found the best evidence yet for emission from a neutron star at the site of a recently observed supernova. The supernova, known as SN 1987A, was a core-collapse supernova, ...
